A Brief Talk on the Detection of Five Tumor Markers

Source: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1671553660437343552&wfr=spider&for=pc
1、What are the five tumor markers?
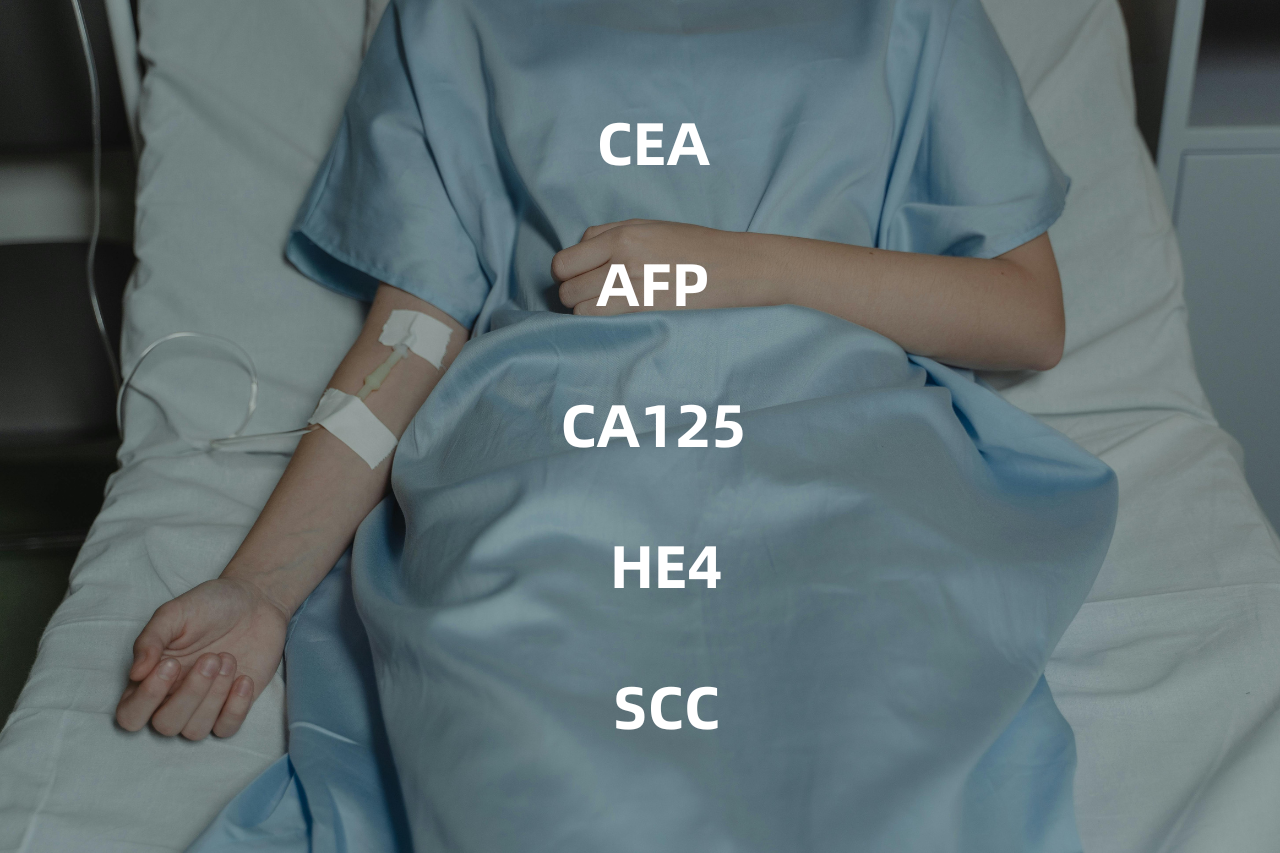
Five tumor markers refer to a group of commonly used tumor marker testing items, which are designed to assist in the diagnosis and monitoring of certain types of cancer through blood testing. These markers typically include five proteins or other molecules associated with different cancers, which may show abnormally high levels in the blood of cancer patients. The five tumor markers generally include the following markers:
01、Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA): CEA is a glycoprotein normally expressed only in the digestive system of the fetus. In adults, high levels of CEA may be associated with cancers of the digestive system (e.g., colon, rectal, stomach).
02、Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP): AFP is a protein that is normally produced in the body of a fetus and is normally present in very low amounts in the blood of an adult. AFP is a common indicator for detecting liver cancer, and AFP levels in the blood of patients with liver cancer tend to be elevated. In addition to liver cancer, AFP levels may also be elevated due to pregnancy, some liver diseases, reproductive system tumors and other conditions. AFP detection is important for early detection of liver cancer and evaluation of treatment effect, but it needs to be used together with other tests to ensure accuracy.
03、Carbohydrate antigen 125 (CA125): CA125 is a protein in the blood that is the preferred marker for ovarian and endometrial cancer. It should be noted that CA125 is not a specific marker for ovarian cancer, that is, elevated CA125 levels do not necessarily indicate cancer. Similarly, normal CA125 levels do not exclude the possibility of ovarian cancer.
04、Human epididymal protein 4 (HE4): HE4 was originally found in human epididymal epithelial cells, and later studies found that it was abundantly expressed in ovarian cancer. At present, HE4 is considered to be a new serum marker of ovarian cancer, a sensitive index for detecting ovarian cancer, and one of the tumor markers. HE4 is another highly recognized tumor marker of epithelial ovarian cancer after CA125.
05、Squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC): SCC is a tumor marker associated with squamous cell carcinoma. It is a glycoprotein present in the cytoplasm of squamous cell carcinoma of the uterus, cervix, lung, head and neck. SCC is involved in the inhibition of apoptosis and differentiation of the squamous epithelial layer in normal squamous epithelial cells and in tumor growth in tumor cells. SCC is mainly used to assist in the diagnosis of cancers of squamous cell origin, such as cervical cancer, lung squamous cell carcinoma, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, nasopharyngeal cancer and vulvar squamous cell carcinoma.
2、The role of tumor markers?
The main function of the five tumor markers is to assist in the diagnosis of cancer and monitor the therapeutic effect. Specifically:
- Auxiliary diagnosis: Although the five tumor markers cannot be used alone to diagnose cancer, they can be used as part of the doctor’s diagnosis. If the level of a marker is abnormally high, it may indicate the need for further investigation, such as imaging studies or biopsy.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment: During the treatment of cancer patients, regular testing of the five tumor markers can help doctors evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. If the level of the marker drops, it may mean that the treatment is working. Conversely, if the level rises, it may indicate a worsening of the condition.
- Adults over 40 years old: The risk of cancer increases with age, so people in this age group should consider regular screening for tumor markers.
- People with a family history of cancer: Certain types of cancer may have a genetic predisposition, so people with a family history of cancer should be screened regularly.
- People with specific risk factors, such as long-term smokers, workers exposed to harmful chemicals for a long time, and people with a history of chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis, have a higher risk of cancer due to environmental or lifestyle factors.
- People with cancer signs in the body: If the body has abnormal symptoms, such as persistent cough, unexplained weight loss, abnormal bleeding, etc., tumor markers should be tested.
- People living in areas with high incidence of cancer: In some areas, the incidence of cancer may be high due to factors such as environment and dietary habits. Residents living in these areas should consider regular screening.
- Adults over 40 years old: The risk of cancer increases with age, so people in this age group should consider regular screening for tumor markers.
- People with a family history of cancer: Certain types of cancer may have a genetic predisposition, so people with a family history of cancer should be screened regularly.
- People with specific risk factors, such as long-term smokers, workers exposed to harmful chemicals for a long time, and people with a history of chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis, have a higher risk of cancer due to environmental or lifestyle factors.
- People with cancer signs in the body: If the body has abnormal symptoms, such as persistent cough, unexplained weight loss, abnormal bleeding, etc., tumor markers should be tested.
- People living in areas with high incidence of cancer: In some areas, the incidence of cancer may be high due to factors such as environment and dietary habits. Residents living in these areas should consider regular screening.
- Adults over 40 years old: The risk of cancer increases with age, so people in this age group should consider regular screening for tumor markers.
- Adults over 40 years old: The risk of cancer increases with age, so people in this age group should consider regular screening for tumor markers.
Prognostic assessment: Levels of certain markers can also help physicians assess a patient’s prognosis. For example, a high level of CEA may indicate a poor prognosis.
3、Does the elevation of tumor markers represent cancer?
Elevated tumor markers do not necessarily indicate cancer. Although the levels of tumor markers may be elevated in some cancer patients, they are not absolutely specific, that is to say, there may be many reasons for the elevation of tumor markers, which does not necessarily mean that there is cancer. There are mainly non-cancer diseases, benign lesions, other diseases, physiological changes, false positive results and so on.
Therefore, the detection results of tumor markers need to be combined with the clinical signs, signs and other examination results (such as imaging examination, pathological examination, etc.). If the tumor marker is elevated, the doctor will usually recommend further tests to determine whether there is cancer or other health problems. In conclusion, the elevation of tumor markers is a warning sign that requires further diagnosis and evaluation, but it is not the same as the diagnosis of cancer. If you have any doubts or concerns, you should consult medical professionals in a timely manner.

4、Which groups need regular screening for tumor markers?
01、Adults over 40 years old: The risk of cancer increases with age, so people in this age group should consider regular screening for tumor markers.
02、People with a family history of cancer: Certain types of cancer may have a genetic predisposition, so people with a family history of cancer should be screened regularly.
03、People with specific risk factors, such as long-term smokers, workers exposed to harmful chemicals for a long time, and people with a history of chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis, have a higher risk of cancer due to environmental or lifestyle factors.
04、People with cancer signs in the body: If the body has abnormal symptoms, such as persistent cough, unexplained weight loss, abnormal bleeding, etc., tumor markers should be tested.
05、People living in areas with high incidence of cancer: In some areas, the incidence of cancer may be high due to factors such as environment and dietary habits. Residents living in these areas should consider regular screening.

Bio-Mapper tumor marker
As the upstream core raw material supplier of in vitro diagnosis, Bio-Mapper adheres to the goal of “customer-centered, R & D and production of the world’s top products, striving to be a deep partner of IVD enterprises”, and is committed to improving medical efficiency, reducing medical costs and promoting the upgrading of the industry from treatment to prevention through continuous technological innovation and platform exploration. To this end, Bio-Mapper independently develops related tumor markers for five conventional tumor markers (CEA, AFP, CA125, HE4 and SCC), with stable product performance and wide application platform.
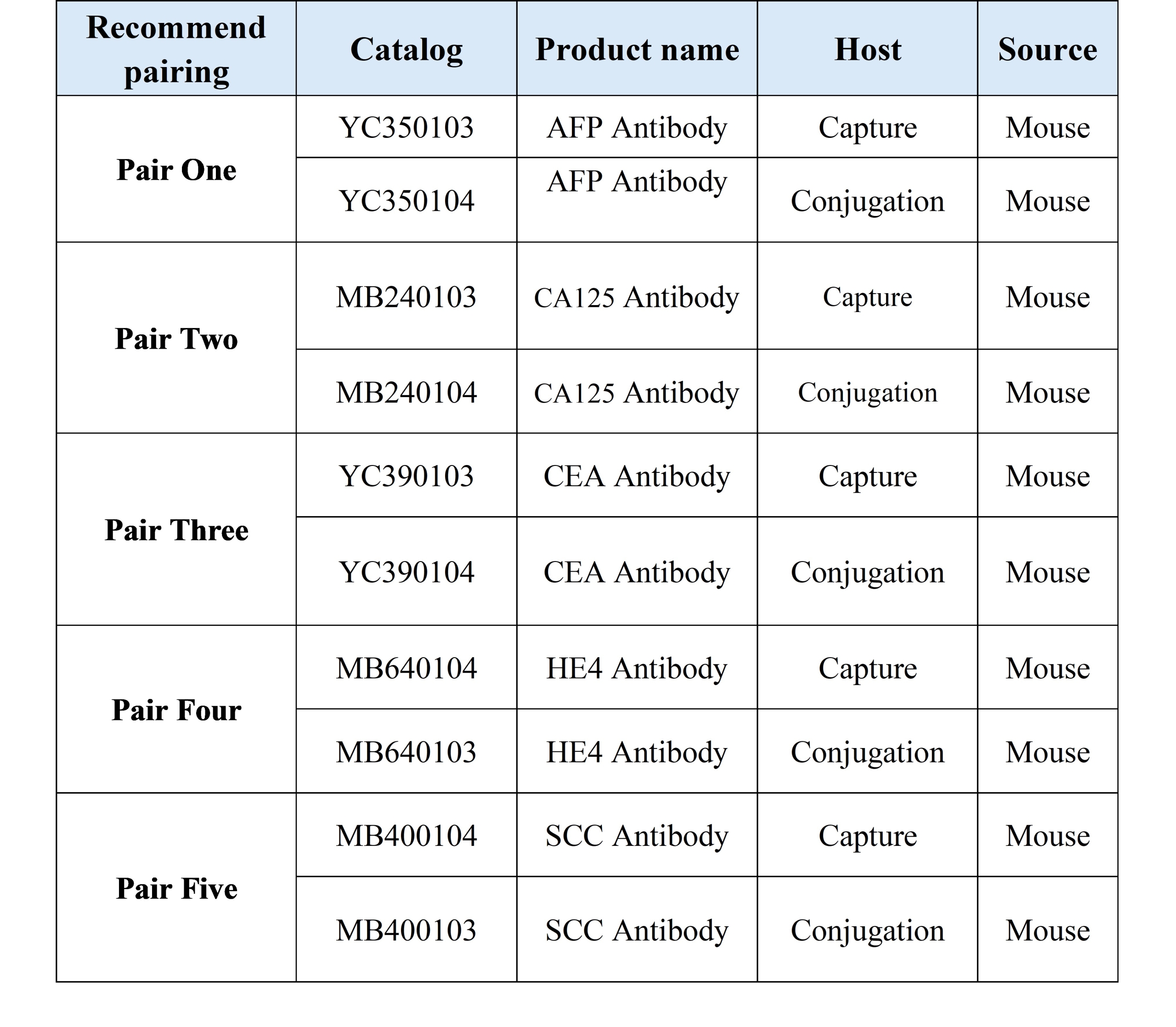
AFP product performance demonstration
- The comparison results of AFP and industry benchmark kits are as follows:
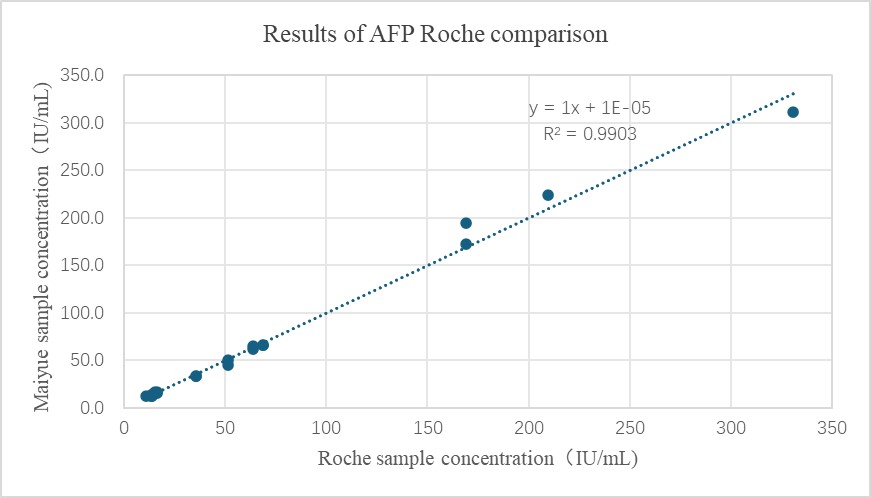
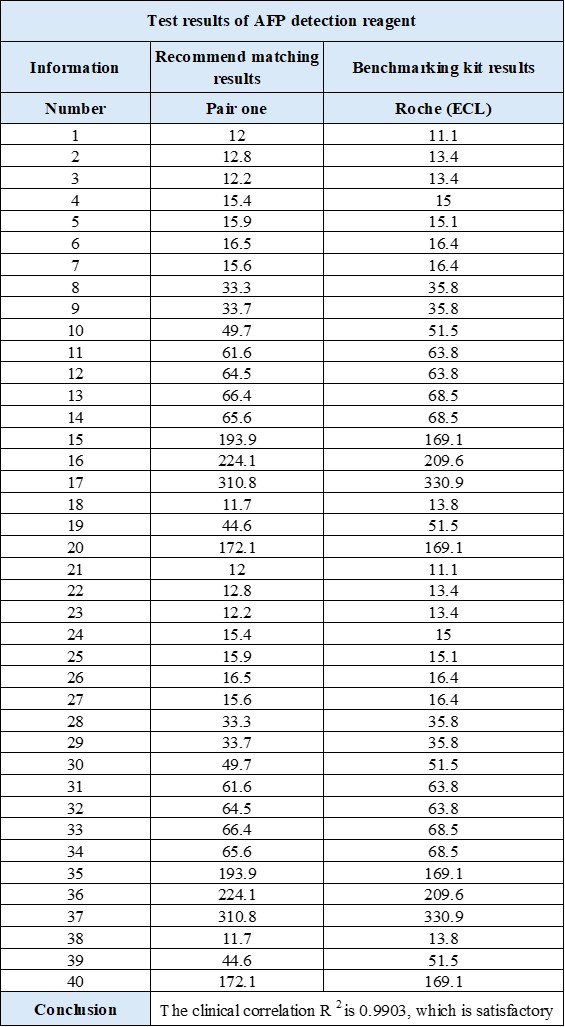
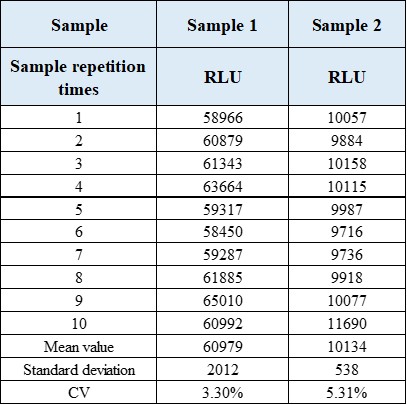
- Reagent performance results
2.1 Repeatability
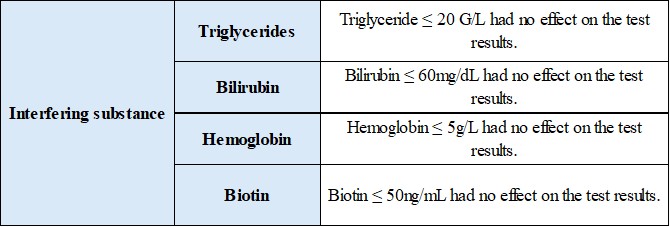
2.2 Anti-interference performance
3. Stability Test Results
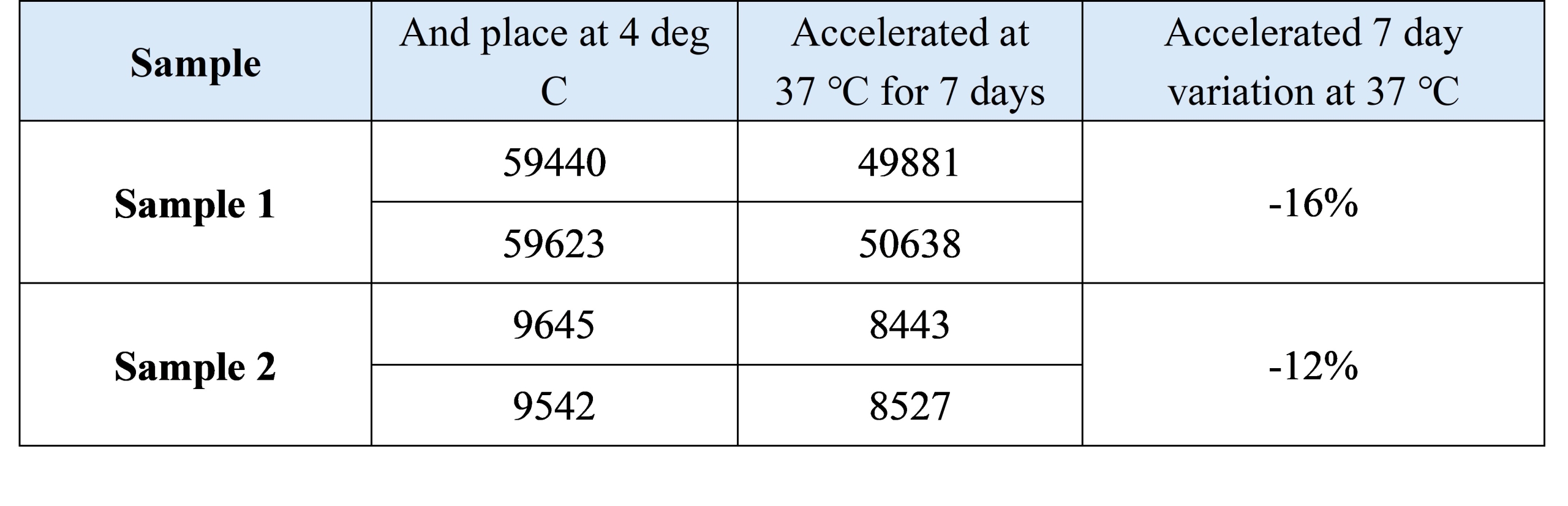
3.1 Thermal stability of reagents
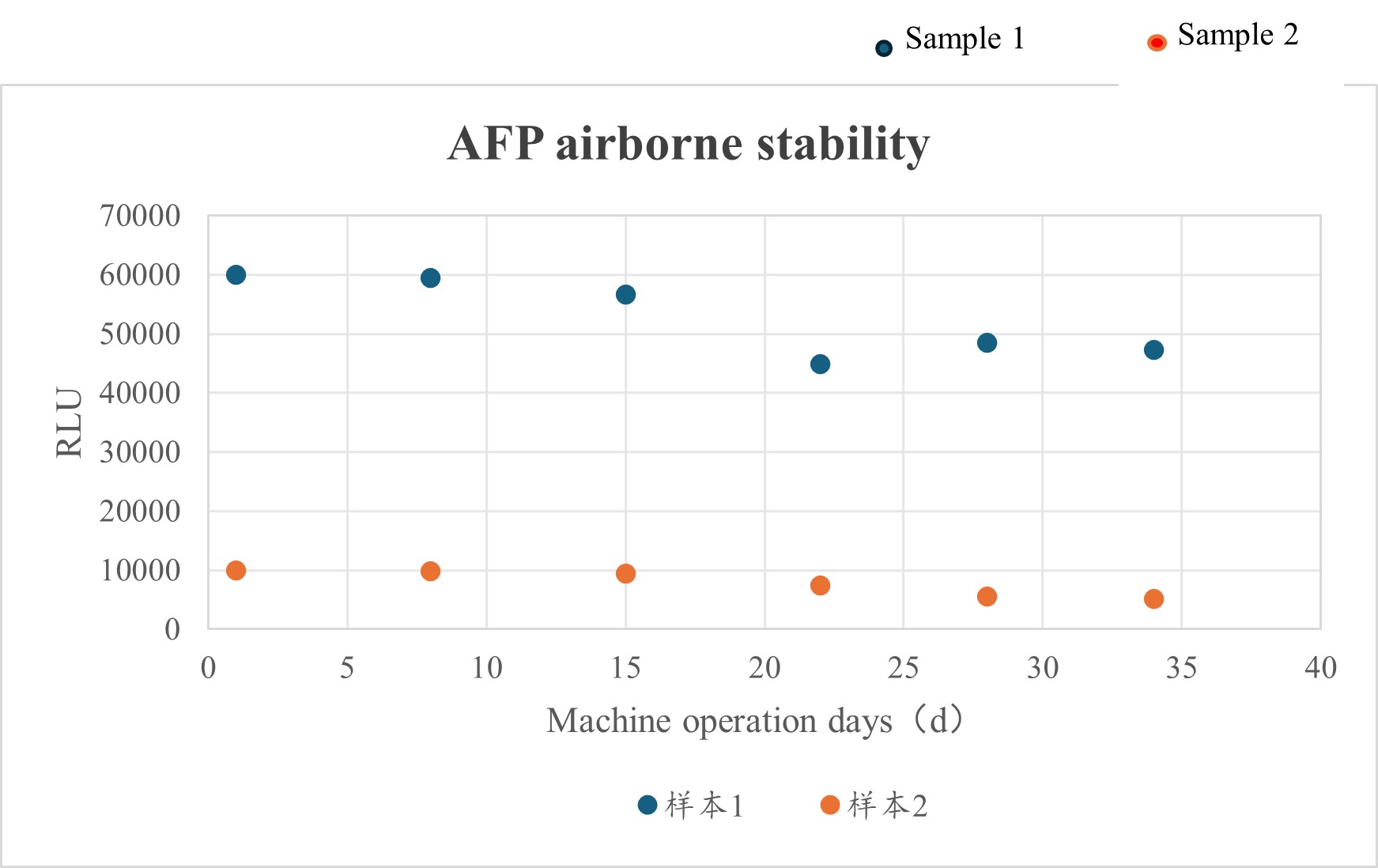
3.2 On-board stabilization of reagents
If you would like to view the performance of other products, please contact us!