Basic Knowledge about Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is an acute infectious disease caused by the dengue virus, primarily transmitted to humans through mosquitoes. The dengue virus is mainly spread by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes, which are types of mosquitoes that thrive in stagnant water environments. Therefore, tropical and subtropical regions, especially those with warm climates and high humidity, are the high-risk areas for dengue fever.
The primary mode of dengue transmission is through mosquitoes biting an infected person and then biting another person to spread the virus. When the dengue virus is present in an infected person’s blood, mosquitoes that feed on them become infected and inject the virus into new hosts when they bite. Additionally, dengue virus can also be transmitted through blood transfusions, organ transplants, and vertical transmission (from mother to baby).
The symptoms of dengue fever vary widely, ranging from mild fever, headaches, and muscle pain to severe bleeding, organ damage, and even death. Infected individuals typically experience symptoms within 3-7 days after infection, with some individuals experiencing high fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and a rash. In some cases, dengue fever can progress to severe dengue, causing internal bleeding, organ failure, and death.
Early diagnosis is crucial for the treatment and management of dengue fever. Since the symptoms of dengue fever resemble those of other illnesses such as influenza and other viral infections, early diagnosis can help doctors quickly identify the cause and implement appropriate treatment measures. Furthermore, early diagnosis can reduce the risk of virus transmission and prevent the escalation of an outbreak. Therefore, understanding the symptoms of dengue fever and the importance of early diagnosis is essential for protecting our own health and the health of others.

Diagnosis Methods for Dengue Fever
A.Laboratory Testing
1.Serological Testing: This method involves detecting dengue virus antibodies in the patient’s blood to determine infection. It can differentiate between different dengue virus serotypes and can be conducted around one week after infection. The advantage is its high sensitivity and specificity, allowing for accurate dengue fever diagnosis. The drawback is that it requires specialized laboratory equipment and techniques, is time-consuming, and is not suitable for urgent diagnoses.
2.Viral Nucleic Acid Testing: This method involves detecting dengue virus genetic material (nucleic acids) in the patient’s blood or other bodily fluids to determine infection. This method has high sensitivity and specificity and can be performed early after infection. The benefits include speed and accuracy, making it suitable for urgent diagnoses. The downside is that it requires laboratory equipment and technical support, making it relatively costly.
B.Clinical Symptom Assessment
1.Clinical Observation of Symptoms: Diagnosis is based on the patient’s symptoms and physical signs to determine potential dengue virus infection. Common symptoms include fever, headache, muscle pain, and rash. The advantage is simplicity and convenience, making it useful for initial assessment. The drawback is that the symptoms lack specificity and can be easily confused with other viral infections.
2.Clinical Scoring Systems: These systems involve using specific scoring criteria based on the patient’s symptoms and signs to assess potential dengue virus infection. Factors like duration of fever, platelet count, and bleeding symptoms are considered, and corresponding scores are assigned to judge the severity of the patient’s condition. The benefit is simplicity and speed, suitable for initial screening. However, the limitation is the relatively limited accuracy of scoring systems, which cannot replace laboratory testing.
Introduction to Rapid Dengue Fever Diagnosis
Rapid dengue fever diagnosis is based on immune chromatography technology, utilizing specific antibodies to detect the presence of the dengue virus in a patient’s body. The principle involves binding the patient’s blood sample with antibodies on a diagnostic strip, forming specific antigen-antibody complexes. When the dengue virus is present in the blood, this complex generates visible color reaction lines, confirming whether the patient is infected with the dengue virus.
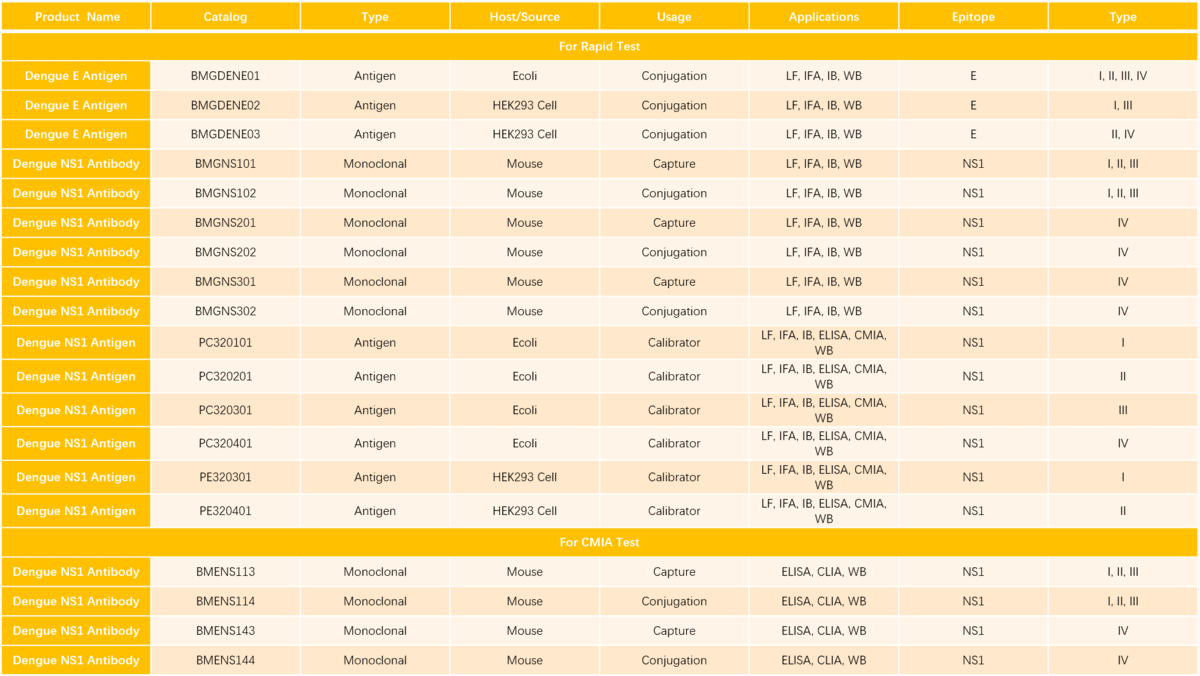
As a leading provider of diagnostic antigens and antibody materials with expertise and advanced technology, Biomapper leverages its proprietary research and development platform, combining previous experience to develop Dengue Virus Type 1/2/3/4 NS1 Proteins (DENV1/2/3/4-NS1), and Dengue Fever Series Diagnostic Uncut Sheet applicable to immune chromatography/ELISA platforms. These products fulfill research needs for downstream manufacturers. We warmly welcome international clients to inquire and visit!
Compared to traditional laboratory testing methods, our dengue fever rapid test uncut sheets and IVD raw materials offer several advantages:
· High Accuracy: Our uncut sheets and raw materials have been validated multiple times, providing accurate results within minutes, significantly reducing diagnosis time.
· Easy Operation: Dengue raw materials come with Certificate of Analysis (COA) documents, making them user-friendly without requiring complex procedures or specialized technical knowledge. This saves downstream manufacturers valuable time and effort.
· High Sensitivity and Specificity: Our lateral flow assay uncut sheets and raw materials exhibit high sensitivity and specificity, accurately detecting the presence of the dengue virus. This means our products can effectively rule out the possibility of other diseases, providing more reliable diagnostic results.
· Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to traditional laboratory testing methods, our Dengue uncut sheets, antigens and antibodies are more cost-effective. This is a crucial consideration for resource-limited regions and medical institutions.
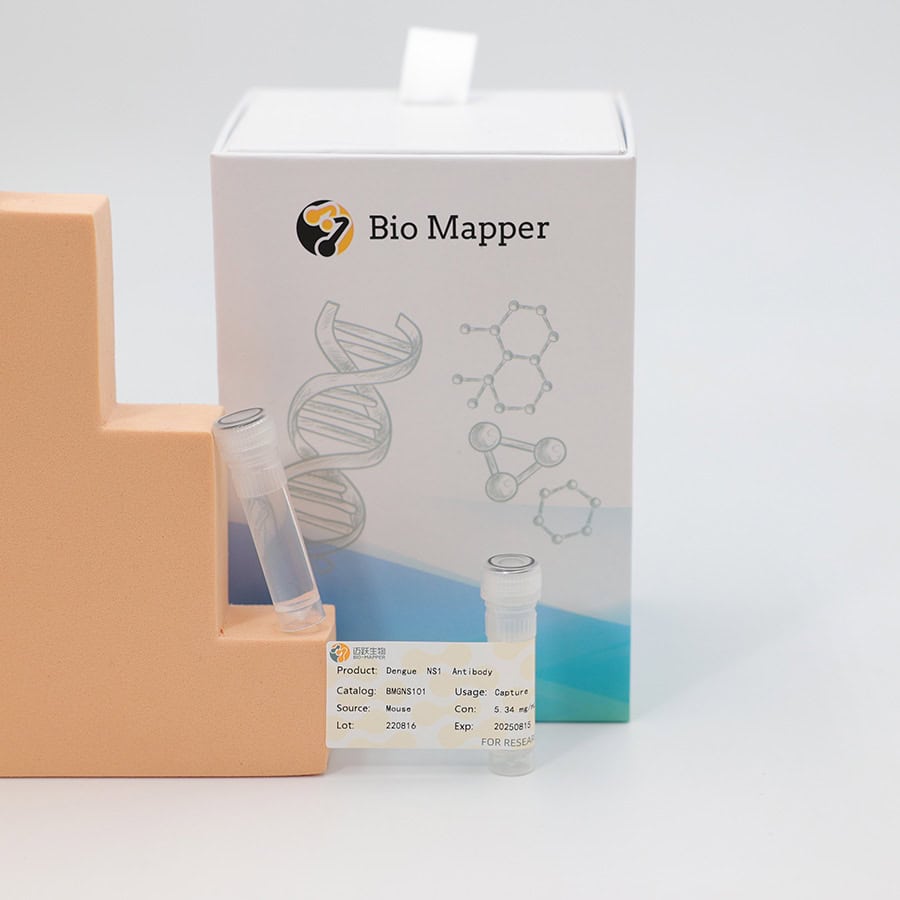

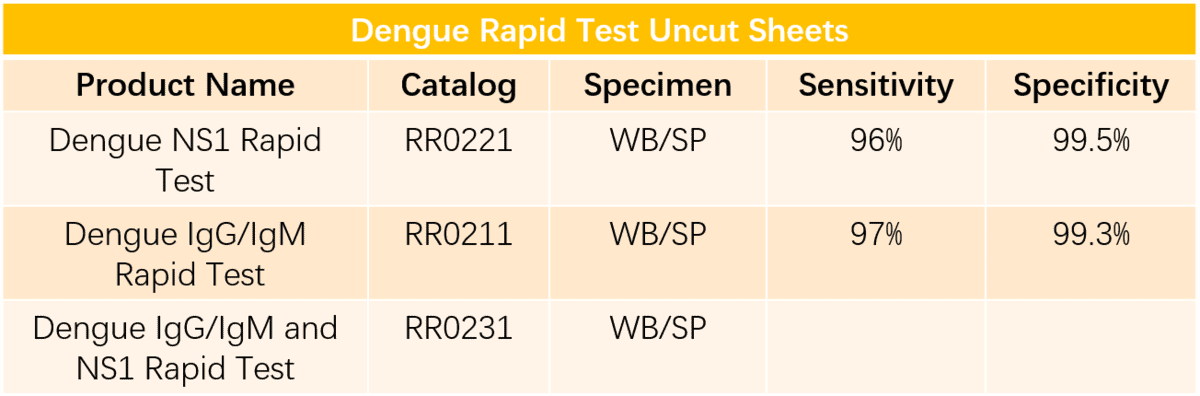
Recommendation for Dengue Uncut Sheets and Raw Materials