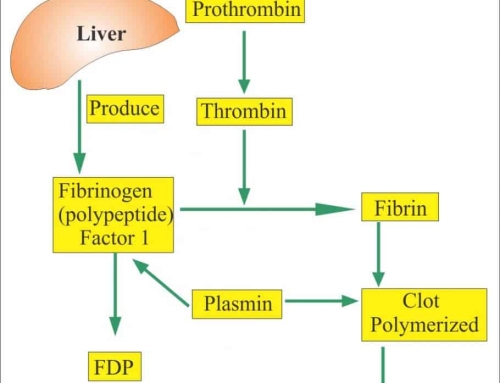
Colloidal gold is a commonly used labeling technique. it is a new type of immune labeling technique using colloidal gold as a tracer marker for antigen antibodies, and has its unique advantages. has been widely used in various biological studies in recent years. almost all immunoblotting techniques used in the clinic use its markers. It can also be used in flow, electron microscopy, immunity, molecular biology and even biochips.
Since Faulk and Taytor introduced colloidal gold into immunochemistry in 1971, immune colloidal gold technology has been widely used in various fields of biomedicine as a new immunological method. In the medical examination the main applications in the test are immunochromatography and rapid immunogold percolation (dot- immuogold filtration assay DIGFA) for the detection of hbsag, hcg and anti-bistrand dna antibodies, etc., which have the advantages of simplicity, rapidity, accuracy and no contamination.
Detection principle
colloidal gold can be polymerized into a certain size of gold particles by chloric acid (haucl4) under the action of reducing agents such as white phosphorus, ascorbic acid, sodium citrate, tannic acid, etc. and because of the electrostatic action, it becomes a stable colloidal state and forms a hydrophobic colloidal solution with negative charge. it is called colloidal gold because of the electrostatic action. colloidal gold is negatively charged in a weakly alkaline environment and can form a firm binding to the positively charged groups of protein molecules. since this binding is electrostatic, it does not affect the biological properties of proteins.
In addition to binding to proteins, colloidal gold can be linked to many other biomolecules combination, such as SPA, PHA, ConA, etc. based on some physical properties of colloidal gold, such as high electron density, particle size, shape, and color responses, coupled with the immune and biological properties of the conjugates, colloidal gold is widely used in immunology, histology, pathology, and cell biology.
Colloidal gold labeling, in essence, is the coating process in which polymers such as proteins are adsorbed on the surface of colloidal gold particles. the adsorption mechanism may be the colloidal gold particle surface negative charge, and the positive charge groups of the protein form a firm binding due to electrostatic adsorption. Various sizes of chloric acid can be easily prepared by reduction method. that is, colloidal gold particles of different colors. this spherical particle has a strong adsorption function to protein and can be noncovalently conjugated with staphylococcal a protein, immunoglobulin, toxin, glycoprotein, enzyme, antibiotics, hormones, bovine serum albumin polypeptide conjugates, and thus become very useful tools in basic research and clinical experiments.
Immunogold labeling technique mainly utilizes the properties of gold particles with high electron density. At the junction of gold-labeled proteins, dark brown particles are visible under the microscope when these markers are in the phase The reaction can also be amplified by the deposition of silver particles, called immunogold and silver staining, because red or pink spots are visible to the naked eye when the ligands should be massed.
Common detection techniques
Immunocolloid staining
cell suspension smears or tissue sections can be stained with colloidal gold-labeled antibodies, or on the basis of colloidal gold-labeled, enhanced labeling with a silver-contrast solution to deposit reduced silver atoms on the surface of marked gold particles, which can significantly enhance the sensitivity of colloidal gold-labeled.
Immunocolloid gold staining Color method
Colloidal gold-labeled antibodies or antibodies bind to negatively stained virus samples or ultrathin sections of tissue, and then negatively stain. can be used for virus morphology observation and virus detection.
Spot immunogold filtration
Using the microporous membrane (such as membrane) as the carrier, the antigen or antibody point on the membrane first, after sealing, add the sample to be tested, and then use the antibody labeled with colloidal gold to detect the corresponding antigen or antibody after washing.
Colloidal gold immunochromatography
The specific antigen or antibody was fixed on the membrane in strips, and the colloidal gold labeling reagent (antibody or monoclonal antibody) was adsorbed on the binding pad when the sample was to be tested After adding to the sample pad at one end of the strip, moving forward by capillary action, dissolving the colloidal gold marker reagent on the binding pad and reacting with each other, and then moving to the region of the fixed antigen or antibody, the conjugate of the test object and the gold marker reagent are specifically bound to it and intercepted, gathering on the detection band, and the result of color rendering can be observed by the naked eye. The method has been developed into a diagnostic test paper, which is very convenient to use.
Rapid gold standard reagent technology
A specific antibody is first immobilized in a zone of the acid cellulose membrane when the dried acid cellulose end is immersed in the sample (urine or serum) due to the capillary The sample will move forward along the membrane, and the corresponding antigen in the sample binds specifically to the antibody when it moves to the fixed area. At the same time, the gold particles have the properties of high electron density at the junction of gold standard proteins. red spots are visible to the naked eye when these markers are massed at the corresponding ligands. is both the principle of rapid gold standard detection method. The key point of producing rapid and accurate reagents is whether the sensitivity and specificity of the materials such as monoclonal antibody, polyclonal antibody, antigen, hapten, protein chitosan and colloidal gold can reach the highest standard, which is the best quality of the gold standard reagent Important criteria.